On January 7, 2026, the full results of the large-scale TASTE-2 clinical study were published in The British Medical Journal (BMJ, Impact Factor: 42.7). The study, led by Academician Wang Yongjun and his team at Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, evaluated patients with acute ischemic stroke and provides high-level evidence supporting a combined treatment strategy of cerebral cytoprotection and endovascular thrombectomy (EVT).
The results demonstrate that the addition of edaravone dexborneol, a multi-target cerebral cytoprotective agent, to standard EVT significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving functional independence at 90 days, while maintaining a favorable safety profile.
Figure: The TASTE-2 study was published in The BMJ on January 7, 2026.
Stroke remains the leading cause of death and long-term disability among adults in China, with ischemic stroke accounting for approximately 70% of all cases. Endovascular thrombectomy is currently considered the gold standard treatment for patients with acute large-vessel occlusion. Despite high rates of successful recanalization (70%–90%), nearly half of treated patients continue to experience moderate to severe disability. Strategies to further protect ischemic brain tissue and reduce post-stroke disability therefore remain a major global clinical challenge.
Study Design and Primary Outcomes
TASTE-2 was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted at 106 centers across China. A total of 1,362 patients with acute ischemic stroke due to large-vessel occlusion were enrolled. All participants underwent EVT within 24 hours of symptom onset and were randomly assigned to receive either edaravone dexborneol or placebo, initiated prior to thrombectomy and continued for approximately two weeks.
The primary endpoint was functional independence at 90 days, defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0–2. The results showed that patients treated with edaravone dexborneol achieved a significantly higher rate of functional independence at 90 days compared with the placebo group. No statistically significant differences were observed between the two groups with respect to mortality, serious adverse events, or other key safety outcomes.
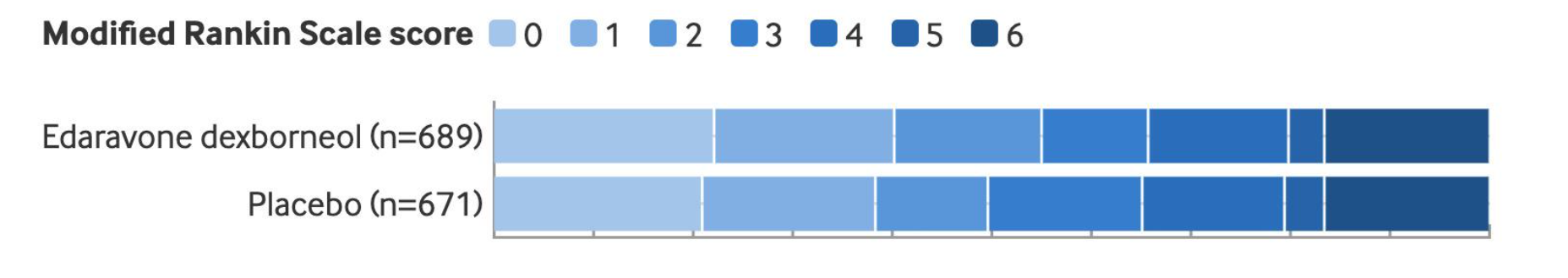
Figure: The proportion of patients achieving functional independence (90-day mRS 0–2) was higher in the edaravone dexborneol group (55.0%) than in the placebo group (49.6%) (P = 0.047).
Subgroup analyses indicated that patients presenting with a mismatch between imaging findings and clinical symptoms derived greater benefit from treatment (55.5% vs. 42.9%). These findings suggest that early administration of edaravone dexborneol before EVT may help preserve ischemic penumbral tissue by attenuating ischemia-reperfusion injury and secondary inflammatory responses.
The results also support a shift in acute ischemic stroke management from an exclusive focus on the “time window” to a more individualized, tissue-based approach. For patients with significant imaging-clinical mismatch, combination therapy integrating cerebral cytoprotection with reperfusion strategies may offer additional functional benefits.
“The results of the TASTE-2 study are very encouraging,” said Professor Wang Chunjuan of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, the first author of the publication. “This rigorously designed, large-scale clinical trial provides evidence that adding a multi-target brain-protective therapy to effective vascular recanalization can further improve functional outcomes in patients. It reflects an evolving treatment paradigm that gives equal weight to restoring blood flow and protecting brain tissue.”
About Edaravone Dexborneol
Sanbexin® (edaravone dexborneol concentrated solution for injection) is a multi-target cerebral cytoprotective agent independently developed by Simcere and approved in China as a National Class 1 innovative drug. It combines edaravone and dexborneol, both of which are capable of crossing the blood–brain barrier and exert synergistic anti-inflammatory and free radical-scavenging effects to mitigate ischemic brain injury.
Since 2015, it has been the only innovative drug approved for stroke treatment globally. Its development spanned more than 12 years and received support twice from China’s National “Major New Drug Development” Program.
Previous studies led by Professor Wang Yongjun (TASTE) and Professor Fan Dongsheng (TASTE-SL) demonstrated the efficacy of injectable and sublingual tablet formulations of edaravone dexborneol in non-thrombectomy acute ischemic stroke patients. These results were published in STROKE (2021) and JAMA Neurology (2024), respectively. The sublingual tablet formulation has also received Breakthrough Therapy designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, marking a milestone for innovative stroke therapies.
The TASTE-2 study provides robust clinical evidence that patients with acute ischemic stroke can derive additional benefit from edaravone dexborneol administered prior to thrombectomy. By expanding the evidence base for cerebral cytoprotection in the context of reperfusion therapy, this study is expected to support broader adoption of combination treatment strategies and contribute to improved functional outcomes and reduced disability following stroke.